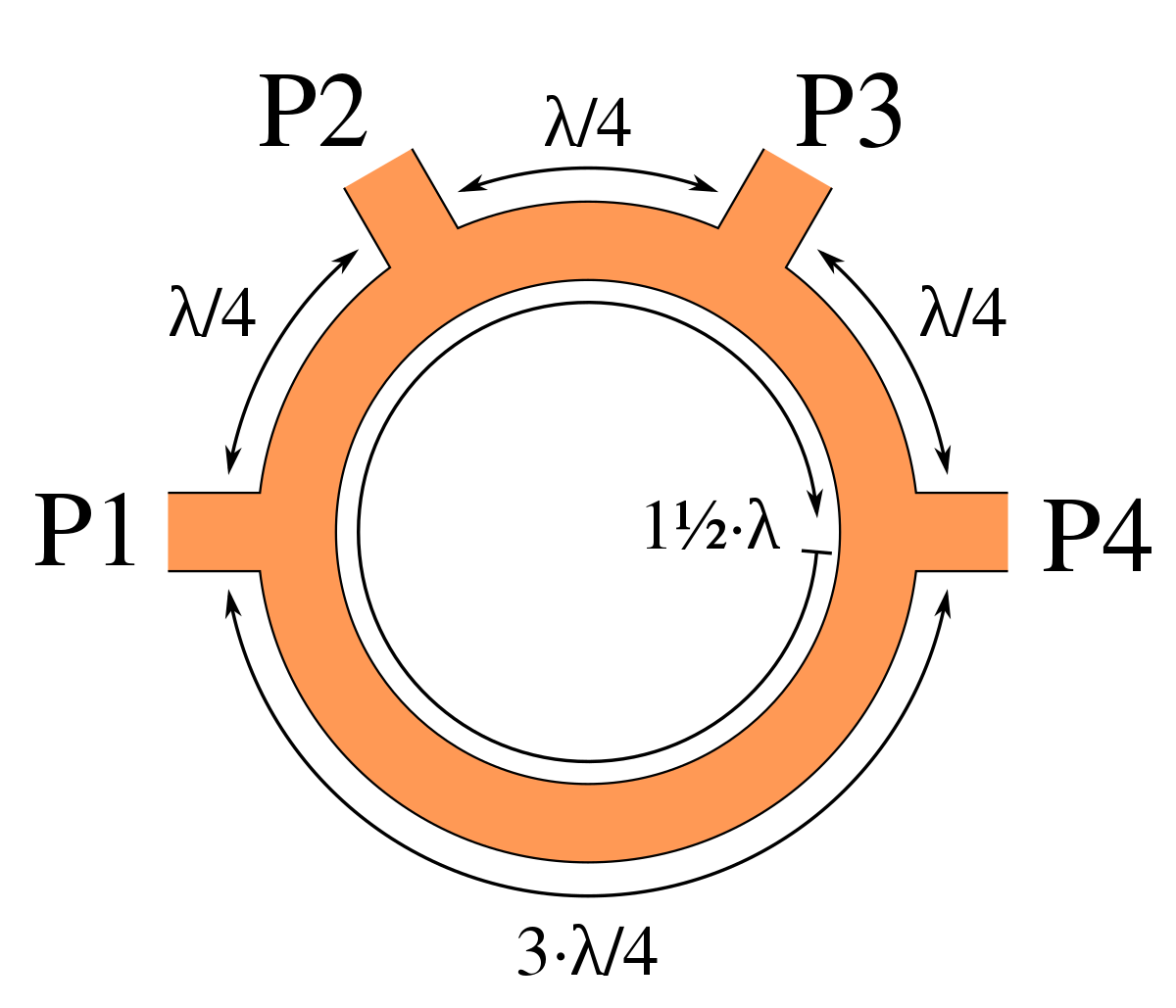
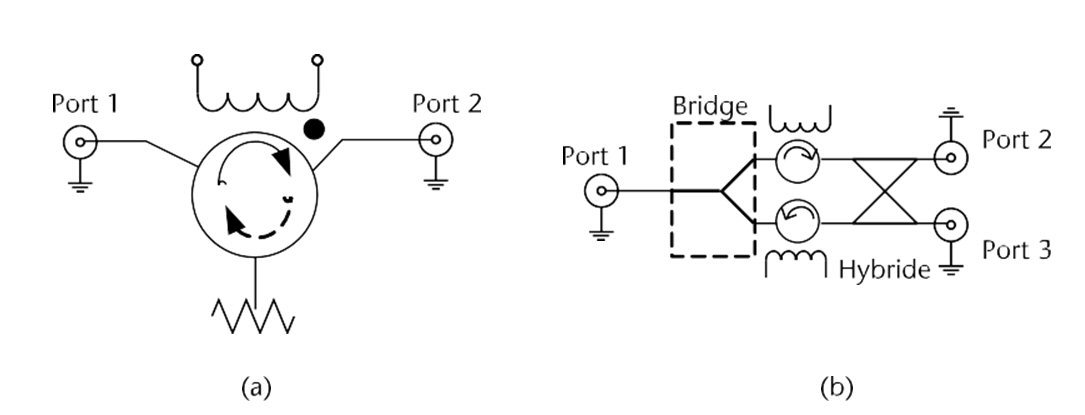
Circulator In Microwave Principle
The way the circulator is constructed it latches into a particular orientation and will stay there in the absence of the electrical signal say for.
Circulator in microwave principle. The following information has been compiled from many technical papers. Due to internal behavior the propagation in one direction is allowed while the other direction is blocked. Though it may seem strange they use ferromagnetic materials. The isolation is typically 60 db and the insertion loss 1 db.
Circulators are non reciprocal devices meaning their behavior in one direction is very different from that in the other direction. Non ferrite circulators are energetic circulators and thus need extra power. A port in this context is a point where an external waveguide or transmission line such as a microstrip line or a coaxial cable connects to the device for a three port circulator a signal applied to port 1. The non reprocity observed in these devices usually comes from the interaction between the propagating wave and the material which can be different with respect to the direction of.
A circulator utilizes a transversely magnetized ferrite junction to circulate incoming microwave energy from port 1 to port 2 port 2 to port 3 and port 3 to port 1. It has been summarized to present a simplified non mathematical description that is used to highlight the operating characteristics of various circulator and isolator types. 3 port circulator s matrix and 4 port circulator s matrix. An isolator is a two port device that transmits microwave or radio frequency power in one direction only.
A really cool type of circulator is a switchable circulator in which an electrical signal is used to switch the orientation of the circulator from cw to ccw and vice versa. The princple of circulator s one way transmission is due to the adoption of ferrite gyromagnetic material. The 3 port circulator is formed by a 120 degree h plane waveguide and the 4 port circulator. The main disadvantage of circulators is based on transistors limitation of power as well as the degradation of the signal to noise s n.
The characteristics of circulator include the following. This material will produce gyromagnetic features also called tensor permeability features if it is under the combined action of high frequency wave field and constant dc magnetic field. When this type of waveguide isolator and circulators is modified it can handle powers in excess of 300 kw pulsed in the x band and much more at lower microwave frequencies. While it is necessary to use scattering parameters s parameters to characterize the isolator or circulator fully their underlying principle is that their material and construction is non reciprocal with a non symmetric scattering matrix.
A circulator is a ferrite device somewhat like a rat race. The main solution for this drawback is varactors.






































_637010935086690049.png)
